Down Syndrome Support
Down syndrome is a genetic condition that results in intellectual and developmental delays. Children with Down syndrome have an extra copy of chromosome 21, which affects their physical and cognitive development. At Kaadir, we understand the unique challenges that come with Down syndrome and are committed to offering the support, therapy, and resources necessary to help children with Down syndrome reach their full potential.
What is Down Syndrome?
Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic condition that occurs when there is an extra copy of chromosome 21. This extra chromosome affects how the body and brain develop, leading to intellectual and developmental disabilities. While each child with Down syndrome is unique, common characteristics of the condition include:
- Cognitive Delays: Children with Down syndrome typically experience mild to moderate cognitive delays, which can impact their ability to learn, solve problems, and process information.
- Physical Characteristics: Physical traits often associated with Down syndrome include a flat facial profile, slanted eyes, and a short neck. Children may also experience low muscle tone (hypotonia), which can affect their ability to sit up, crawl, or walk independently.
- Speech and Language Delays: Delays in speech and language development are common, with children experiencing difficulty pronouncing words, understanding language, or expressing themselves clearly.
- Social and Emotional Development: Children with Down syndrome may show strengths in social interactions, such as being affectionate and forming close bonds with family and peers. However, they may also face challenges in adapting to complex social situations.
How Kaadir Supports Children with Down Syndrome
We believe that with the right support, children with Down syndrome can thrive and achieve their fullest potential. Our team of experienced specialists—speech therapists, occupational therapists, and developmental psychologists—works closely with families to provide personalised programs tailored to the specific needs of children with Down syndrome.
Our Approach Includes:
- Comprehensive Developmental Assessments: To accurately identify your child’s strengths and areas of growth, we start with a thorough online assessment. This evaluation helps us understand the specific challenges your child may face and enables us to create a tailored plan to support their development.
- Personalised Therapy Plans: Based on the assessment, we create individualised therapy plans that focus on improving communication skills, motor development, cognitive abilities, and social interaction. These programs aim to enhance your child’s quality of life and encourage them to reach their milestones.
- Speech and Language Therapy: Speech development is often a key area of focus for children with Down syndrome. We provide expert speech therapy to help children improve their ability to speak clearly, understand language, and express themselves.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy is essential for children with Down syndrome to improve their fine motor skills, muscle strength, coordination, and independence in daily activities. Our occupational therapists work to build these skills, helping children gain confidence in performing tasks like feeding themselves, dressing, and handwriting.
- Cognitive Development Support: We work with children to enhance their cognitive abilities, such as memory, attention, and problem-solving. Through interactive activities and targeted exercises, we help children improve their learning and thinking skills.
- Social and Emotional Skills Training: Many children with Down syndrome excel in forming bonds with others, but they may need extra support to understand social cues and develop coping skills. Our programs focus on strengthening social skills, building emotional regulation, and fostering positive interactions with peers and adults.
- Parental Support and Training: We offer workshops and resources to help parents navigate the challenges of raising a child with Down syndrome. These training programs empower families with tools to support their child’s development and foster their independence.
Why Choose Us?
- Expert Professionals: Our team of therapists and specialists has extensive experience working with children with Down syndrome and is equipped with the latest techniques to provide effective, evidence-based interventions.
- Personalised Care: We understand that each child with Down syndrome has unique needs. Our services are customised to meet those needs, ensuring that children receive the most relevant and impactful support.
- Dual-Language Support: We offer services in both English and Arabic, making it easier for families in the Middle East and North Africa to access high-quality care in their preferred language.
- Convenient Access: All of our services are available online, allowing families to access therapy and consultations from the comfort of their homes.
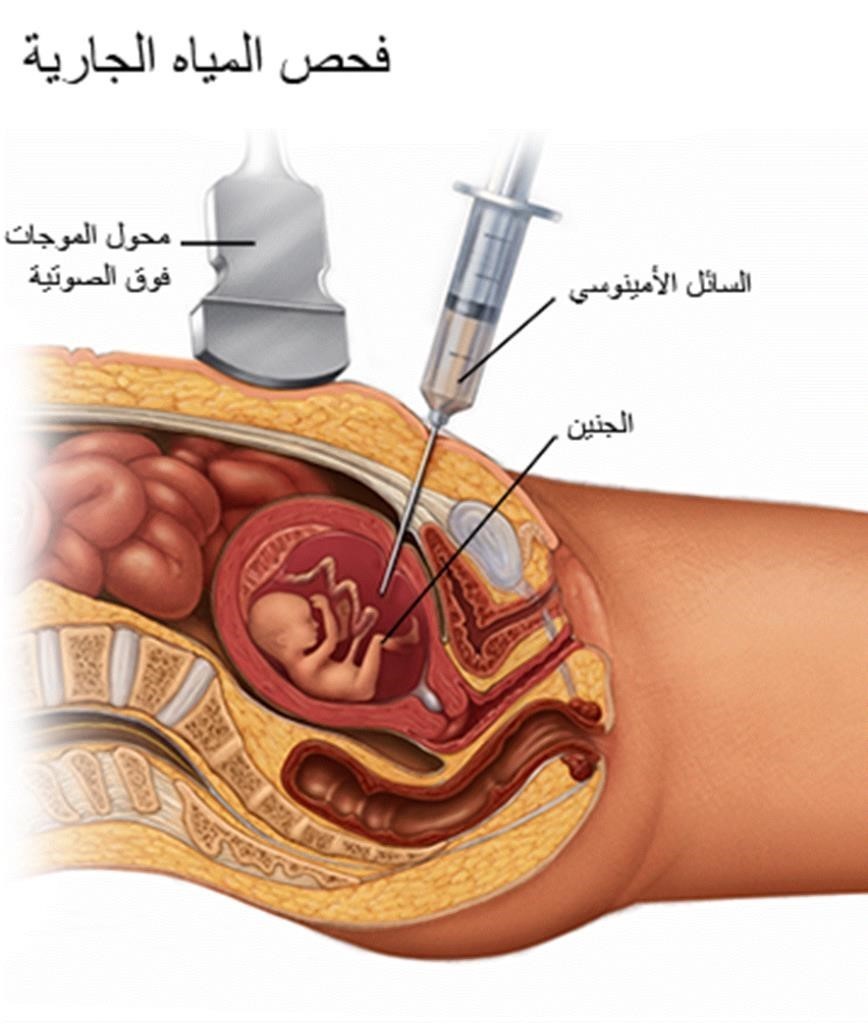
- Amniotic fluid test. A sample of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus is withdrawn through a needle inserted into the mother’s uterus. Then this sample is used to analyze the chromosomes of the fetus. Doctors usually perform this test in the second trimester, after 15 weeks of pregnancy. This test also carries a very low risk of miscarriage
Congratulations, you are Pregnant
You have received the great news; you are pregnant Congratulations.
In the first ten weeks, we don’t expect you to visit our website as the chances of having a typical child is quite high, in America from every 700 children only one child could have down syndrome.
After week ten you will have to go through investigations to check if your child has down syndrome, in some countries, these checks are integral part of pregnancy follow-up routine and is paid by the government, mostly done for females above 35, as the chances are higher to have a baby with down syndrome at this stage. (no confirmed research that age is the main reason for having DS.
SCREENING TESTS DURING PREGNANCY:
Tests are performed for pregnant women to see if the newborn has Down syndrome as a routine part of prenatal care and include screening tests.
FIRST TRIMESTER TEST:
Blood test: This blood test measures the levels of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) and the pregnancy hormone known as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). Abnormal levels of PAPP-A and HCG may indicate a problem with the baby.
Nuchal translucency test: During this test, an ultrasound is used to measure a specific area on the back of your baby’s neck. This is known as a nuchal translucency screening test. When abnormalities are present, more fluid than usual tends to collect in this neck tissue.
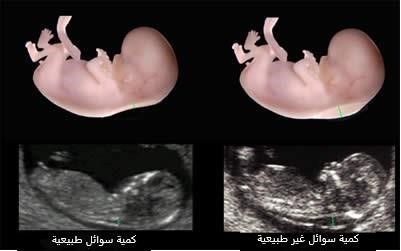
Using your age and the results of the blood test and the ultrasound, your doctor or genetic counsellor can estimate your risk of having a baby with Down syndrome.
If your screening test results are positive or worrisome, or you’re at high risk of having a baby with Down syndrome, you might consider more testing to confirm the diagnosis. Diagnostic tests that can identify Down syndrome include:
SECOND TRIMESTER TEST:
Quadruple examination
It is a blood test that is performed in the second trimester between weeks 15 and 20 in which an examination is performed :
- (Inhibin A) It is a hormone released by the placenta
- Alpha-fetoprotein, a protein produced by the fetus
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), a hormone released by the placenta
- Estriol, a hormone released by the placenta and the baby’s liver
Quadruple screening is used to assess the likelihood of a fetus having Down syndrome. If the screening test results indicate an increased likelihood of having a baby with Down syndrome, you may need to do more tests to confirm the diagnosis. The quad screening test does not pose a risk of miscarriage or other pregnancy complications. Although it is recommended for all pregnant women to take the test, some women should give it a serious thought. These cases include:
- Women over the age of 35 years
- Women with a family history of birth defects
- Women who gave birth to their previous child with a birth defect
- Women who suffer from type 1 diabetes
If the chance of having a child with Down syndrome appears high during prenatal screening, doctors will often advise a mother to undergo diagnostic testing.
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS :
Diagnostic tests that can identify Down syndrome include:
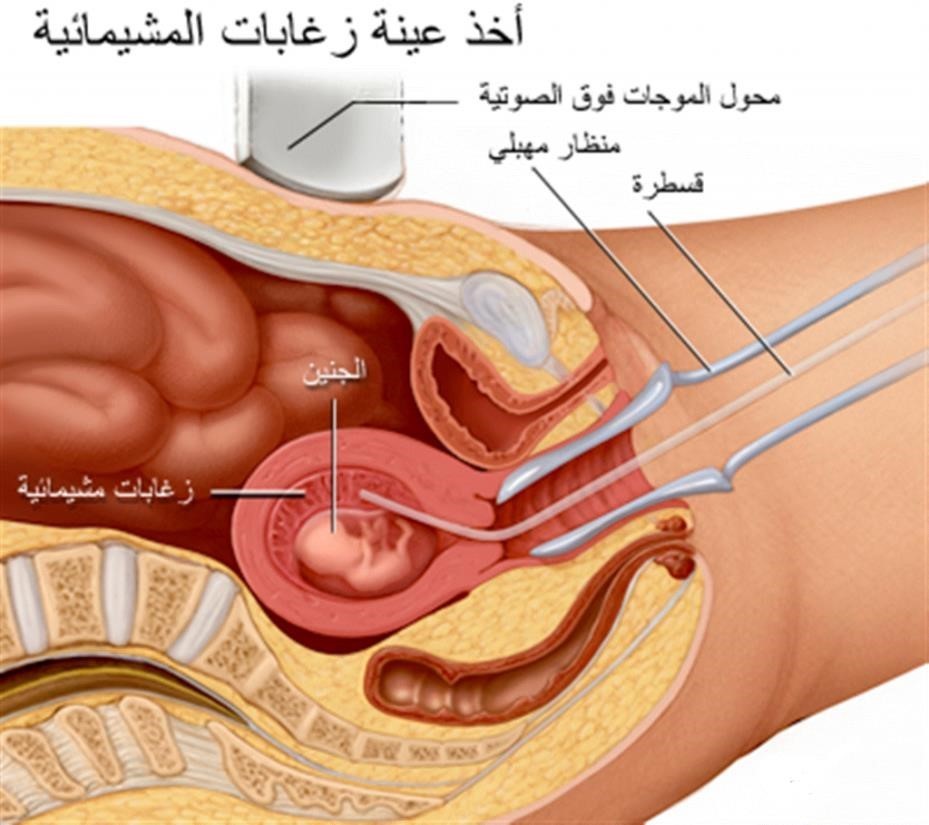
1– Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). In CVS, cells are taken from the placenta and used to analyze the fetal chromosomes. This test is typically performed in the first trimester, between 10 and 13 weeks of pregnancy. The risk of pregnancy loss (miscarriage) from a CVS is very low.
- Amniotic fluid test. A sample of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus is withdrawn through a needle inserted into the mother’s uterus. Then this sample is used to analyze the chromosomes of the fetus. Doctors usually perform this test in the second trimester, after 15 weeks of pregnancy. This test also carries a very low risk of miscarriage
| First- and second trimester screening |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| screen | Week of pregnancy when performed |
Detection rate | False positive | Description |
| Combined test | 10–13.5 wks | 82–87% | 5% | Uses ultrasoun or total beta-h |
| Quad screen | 15–20 wks | 81% | 5% | Measures the |
- DNA tests : This advanced blood test aims to screen for cell-free DNA from the placenta and the fetus in the mother’s bloodstream. It assesses whether the fetus is at risk of Down syndrome or any chromosomal disorder
If you have any questions at this stage, please visit our ASK Specialist section and talk to a specialized physician.
The important fact is that being pregnant with a child with down syndrome is no difference than any typical pregnancy, and no measure differences in the development of your child from any normal pregnancy.
False positive: means that the test result was positive, but the child does not have Down syndrome
At the present time, it is not possible to determine the birth of a child with Down syndrome before pregnancy
To monitor the development of your child in the coming nine months, subscribe to receive a weekly newsletter and learn about the development of your child as well as the possible changes you may see in your body & life
| and inhibin-A | ||||
| Integrated test | 15–20 wks | 94–96% | 5% | Is a combinati |
| Cell-free fetal DNA | From 10 wks | 96–100% | 0.3% | A blood samp analysis. |
Baby Is Finally Here
After Birth
Hi Mamy , Congratulations , you have finally ended the long tough journey of pregnancy and your body is getting back to normal. The back pain and the sallower legs are disappearing and from the first moment you took the bundle of joy in your arms , all the pain has vanished and you completely forgot you were pregnant. Now if this is your first baby, then you must be uncertain of anything and not sure if you can make it, don’t worry this happens to every one even those who gave birth to many kids, every time feels as if it is the first time. Now what makes you special is the fact that your baby is unique and so special. If you knew during pregnancy ,or after birth , in all cases the strange feeling of having a baby who is not as you have always dreamt of is truly difficult .
There is no doubt that many parents feel shocked when their newborn is diagnosed with Down syndrome and find it difficult to deal with it. Feelings of fear and anxiety about the child and his needs, and his state of health, and these emotions may be more intense in mothers, especially immediately after birth. As the news of the birth of a child with Down syndrome is very strong trauma as most families cannot forget this moment even if after several years and they remember As if it happened yesterday, but their eagerness to learn everything related to their children helps them to accept the reality of their child and work to help him
It is important to know that you are not alone and that many people have gone through the experience before you. Before . It is natural to feel anxious about when you look into the future or try to plan for it in terms of family, society, and the possibility of the child changing for the better in the coming years. Instead, try to walk step by step and listen to your child in spite of that.
We have been brought up thinking that life is exactly as we know it , it cant be any different , we will have babies who are healthy , smart and well studied by scientist over time , so they know exactly how they will grow up ,what vaccination they need , and what you should be doing in each milestone of their life. Our babies didn’t get this chance, only recently some studies are made to try and see beyond the lapel of disability and help us embrace this great change , and reshape our dreams to suit our angles
Down syndrome is not a matter of choosing the family, nor shortening it, nor does it necessitate shame, guilt, or denial of its existence. Raising a child with Down syndrome will not differ much from other children except in some aspects that need more attention. It is important to know that nothing can be done to prevent Your child has Down syndrome. Do not be ashamed that you have a special child with Down syndrome.
There are many things that parents can do to help him cope with his condition. The most important of which is that you do not miss any of his medical appointments. Taking your child in care most of the time will help keep him healthy. There are many health problems that your child can encounter at any time in his life. Regular check-ups and tests will help to know if your child has any problems that need treatment. In many cases, your child’s health is better when his health problems are discovered and treated early. It is also important to know that since your child may get the infection easily, it is important for him to get the necessary vaccinations to protect his health.
In Kaadir we shall take this journey with you , trying to find every information or study and present it to you in a way that enables you to live the dream of becoming a mother of a wonderful child. So buckle up and get ready to fly in world of wonder , we are here for you and will do everything in our ability to make you overcome all the challenges of the journey .
Down syndrome features:
Look carefully at your gorgeous baby, you will see the features of down syndrome making him extra awesome. People with Down syndrome may have some or all of these physical characteristics: a small chin, slanted eyes, poor muscle tone, a flat nasal bridge, a single crease of the palm, and a protruding tongue due to a small mouth and relatively large tongue. These airway changes lead to obstructive sleep apnea in around half of those with Down syndrome. Other common features include: a flat and wide face, a short neck, excessive joint flexibility, extra space between big toe and second toe, abnormal patterns on the fingertips and short fingers. Instability of the atlantoaxial joint occurs in about 20% and may lead to spinal cord injury in 1–2%. Hip dislocations may occur without trauma in up to a third of people with Down syndrome
Growth in height is slower, resulting in adults who tend to have short stature—the average height for men is 154 cm (5 ft. 1 in) and for women is 142 cm (4 ft. 8 in). Individuals with Down syndrome are at increased risk for obesity as they age. Growth charts have been developed specifically for children with Down syndrome.
The necessary test:
It is always recommended to undergo a prenatal screening test for genetic conditions of families.
And if Down syndrome is discovered, (Trisomy 21) or any other chromosomal change that causes Down syndrome, by prenatal testing, the family must receive the necessary instructions to explain the problems and know the importance of the procedure Prenatal heart test Because there is a high risk of heart problems at birth with Down syndrome, an echocardiogram during pregnancy (an ultrasound of the heart) can provide information that may be useful for the remainder of pregnancy and childbirth. This information helps in making decisions such as where the baby will be born. And medical services needed late in pregnancy or at birth.
If Down syndrome is diagnosed, before birth or suspected after birth, a complete physical examination should be performed to confirm known physical features and check for any possible associated conditions. To find out more additional tests for newborns, please visit the Useful Health Information page to view the type and timing of the examinations. A diagnosis of Down syndrome, in the prenatal or newborn stage, can cause many concerns for parents. Therefore it may be helpful to speak with the medical genetics team (geneticist) or others the pediatrician recommends.
Newborn diagnostic tests:
After birth, the initial diagnosis of Down syndrome usually depends on the general appearance of the child, but because the facial signs of a child with Down syndrome may also be found in children without the syndrome in some cases, so you will likely be asked to have a test called a chromosomal karyotype. test) to confirm the diagnosis through the use of a blood sample, this test analyzes the child’s chromosomes. If all or some of the cells have an extra copy of chromosome 21, the result of the diagnosis is that of Down syndrome
Down syndrome complications :
Newborns with Down syndrome are more likely to have congenital heart defects, hearing and vision loss, respiratory problems, obstructed gastrointestinal tract obstruction, childhood leukemia, and other health conditions. They may also be exposed to an increased susceptibility to infection. Fortunately, these problems can be addressed. The earlier other medical problems are diagnosed, the greater the chances of them being treated effectively.
As doctors must detect these cases routinely, as some of them, such as heart defects, may be present even if no symptoms appear quickly. Although the list of potential health problems can be daunting, you must bear in mind that your child will not necessarily suffer from all of them, or perhaps any of them. If the child was exposed to one or more of these complications, the level of progress in the field of medicine made most of the cases treatable. For example, most heart conditions can be treated with surgery.
You can ensure the optimal growth of your newborn by providing informed healthcare. There is an overwhelming amount of information available, so it is important not to leave yourself feeling overwhelmed and overwhelmed. You must learn at your own pace, and try to focus on those things that you can do in the meantime to get your child off the right start path.
In order to secure exemplary health care, it makes sense to select a pediatrician who specializes in developing children or a specialist familiar with Down syndrome, if found in your area. However you should bear in mind that it is not always necessary to find a syndrome expert Down. The most important factor, when you have a child with special health care needs, is finding a doctor who is willing to learn about the condition and work with you to ensure the best possible care for your child
You have the right to meet with prospective doctors to choose the best doctor for you. You should search for someone you feel comfortable with, and you can communicate with him freely. It also predicts that you do not feel intimidated when talking to the doctors. A good doctor knows that parents are the experts when it comes to their children. He must respect their concerns and view them as partners.
Steps you should follow :
It is very overwhelming and your mind doesn’t stop thinking of what you should be doing , here is our advise of the very first steps you should take after giving birth to a down syndrome child
Smile , it is a journey , and you will not be alone , you will find support and everything will be OK.
If not done yet , please meet with a pediatrician , he will examine your baby and show you what you should do , ideally he will ask for echo test & his thyroid to be checked.
Tell every one, family , friends colleagues, this will make you feel comfortable , and will take from your head the thinking of what people think and what should I do , just tell them and move on and get ready to focus on your baby development
You should start early intervention program, please look at our early intervention program page & see what you should be doing
Finally enjoy every minute of it , it is quite an experience
Breastfeeding :
Breast milk boosts your baby’s immune system and protects it from many autoimmune disorders such as digestive disorders, asthma and allergies. This is especially important for children with Down syndrome, as they are susceptible to viral and respiratory infections. The process of frequent sucking during breastfeeding strengthens your baby’s lips, tongue and face. This will serve as a starting point for developing his speaking skills in the future. Breastfeeding is convenient! They are always available and contain all the nutrients, calories and fluids your baby needs. The hormones produced during breastfeeding help your uterus shrink to the size it was before pregnancy. Breastfeeding has been shown to reduce the risk of ovarian and breast cancer.
Breastfeeding provides warmth and closeness. Physical contact helps create a special bond between you and your baby’s son. Since babies with Down syndrome, they often have low muscle tension, including reduced muscle tone in their tongues and lips, and the prominence of their tongues. Breastfeeding takes longer, so good head support is especially important for your baby during breastfeeding. There are a variety of ways that you can hold your baby while breastfeeding to support his head, neck and upper back. The gentle, firm support at the base of your baby’s head helps him suck well without getting tired. However, it is important not to put too much pressure on the back of the baby’s head. Vomiting and lack of stool are important early warning signs to watch out for.
Sleep :
Many babies with Down syndrome tend to sleep very much in the first few weeks after birth, which can hinder their breastfeeding process. To ensure your baby is getting enough milk, it may be necessary to wake him up to feed every two hours. It can also be difficult to keep your baby awake throughout the breastfeeding period. The breastmilk obtained in the last part of the breastfeeding contains fats and calories which are important for growth. It is important for your child to receive these nutrients
Dim the room so that your child does not have to close his eyes to the light. Remove his clothes before breastfeeding to keep him cool and alert. You can also stimulate his senses by gently touching the edge of his outer ear, stroking his arms, and talking to him while feeding. These touches and sounds will distract him from drowsiness and help him focus on the current task. Try placing a cool, damp washcloth on your baby’s stomach, legs or forehead. The cold sensation must awaken him. Your baby can be encouraged to continue active breastfeeding and to have more milk, by using the breast pressure method or switch feeding
Guide to using the recommended language:
People with Down syndrome should be referred to as people (people) first.
“A child with Down syndrome” is said to emphasize that he is a child in the first place. Also avoid the phrase “Down Child” or describing the child’s condition as “Down”, such as saying “He has Down.”
Down syndrome is a condition or syndrome, not a disease.
Do not say “suffers from Down syndrome”, as he is a person who has a syndrome and does not suffer from it.
It is preferable to use the term “normal growth” rather than “natural growth.”
Replace the term “mental retardation” with “intellectual disability” as the appropriate term.
The National Down Syndrome Association strongly condemns the use of the word “retarded” in any derogatory context. The use of this word is harmful, traumatic, and leads to the belief that people with special needs are incompetent.
The United Nations has called on all countries of the world to stop using the word Mongolian and to use the word Down syndrome on these children, noting that European countries are suing anyone who uses the old word “Mongolian”.
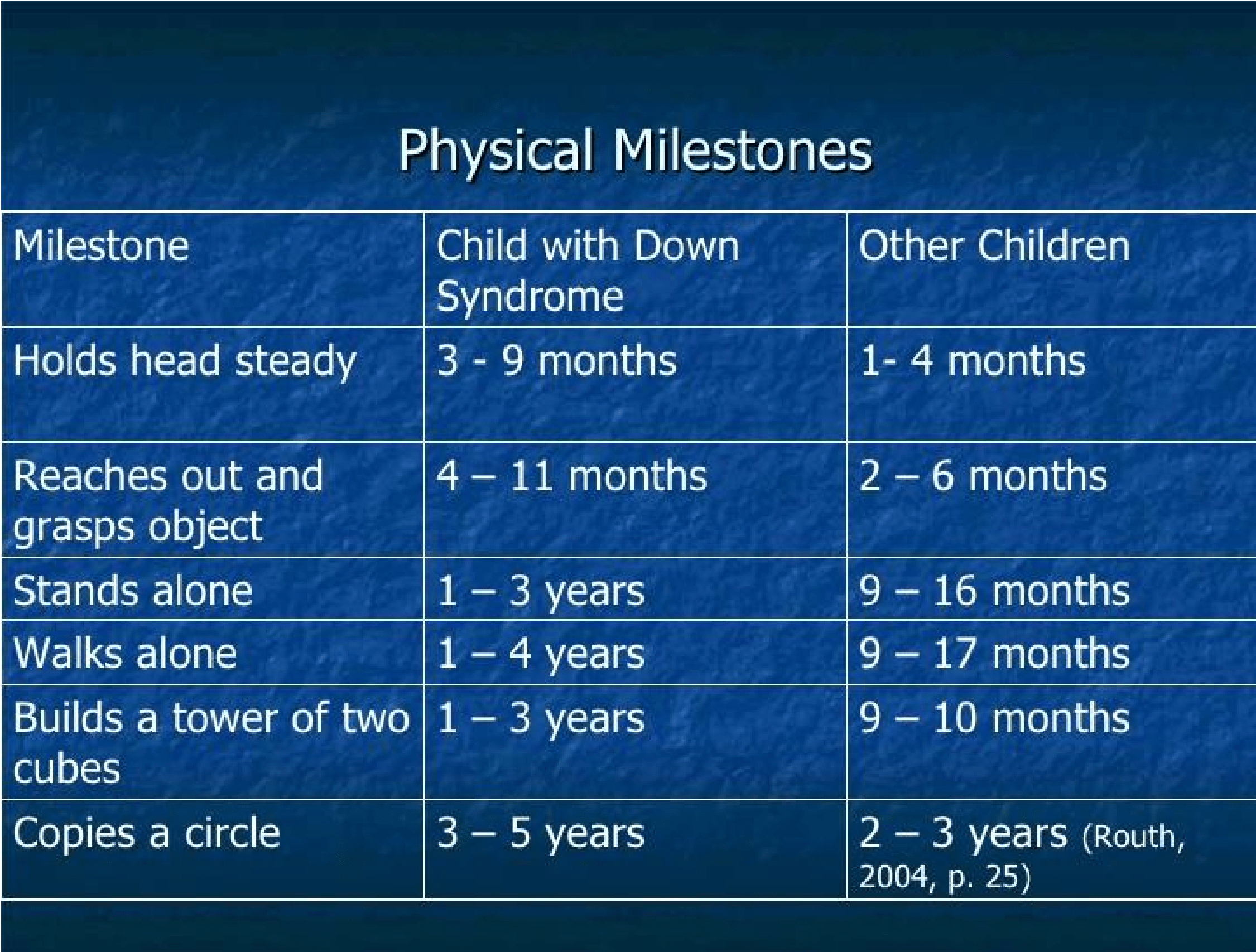
Childhood & Skill Development
children with the Children with the syndrome are as different from each other as all children. However, by and large, their development is slower than that of most children . The character below will guide you to the expected physical development milestones ( Please note that every child develop at own base, and may not develop as the below chart, but this chart gives a prospective to how they may develop.
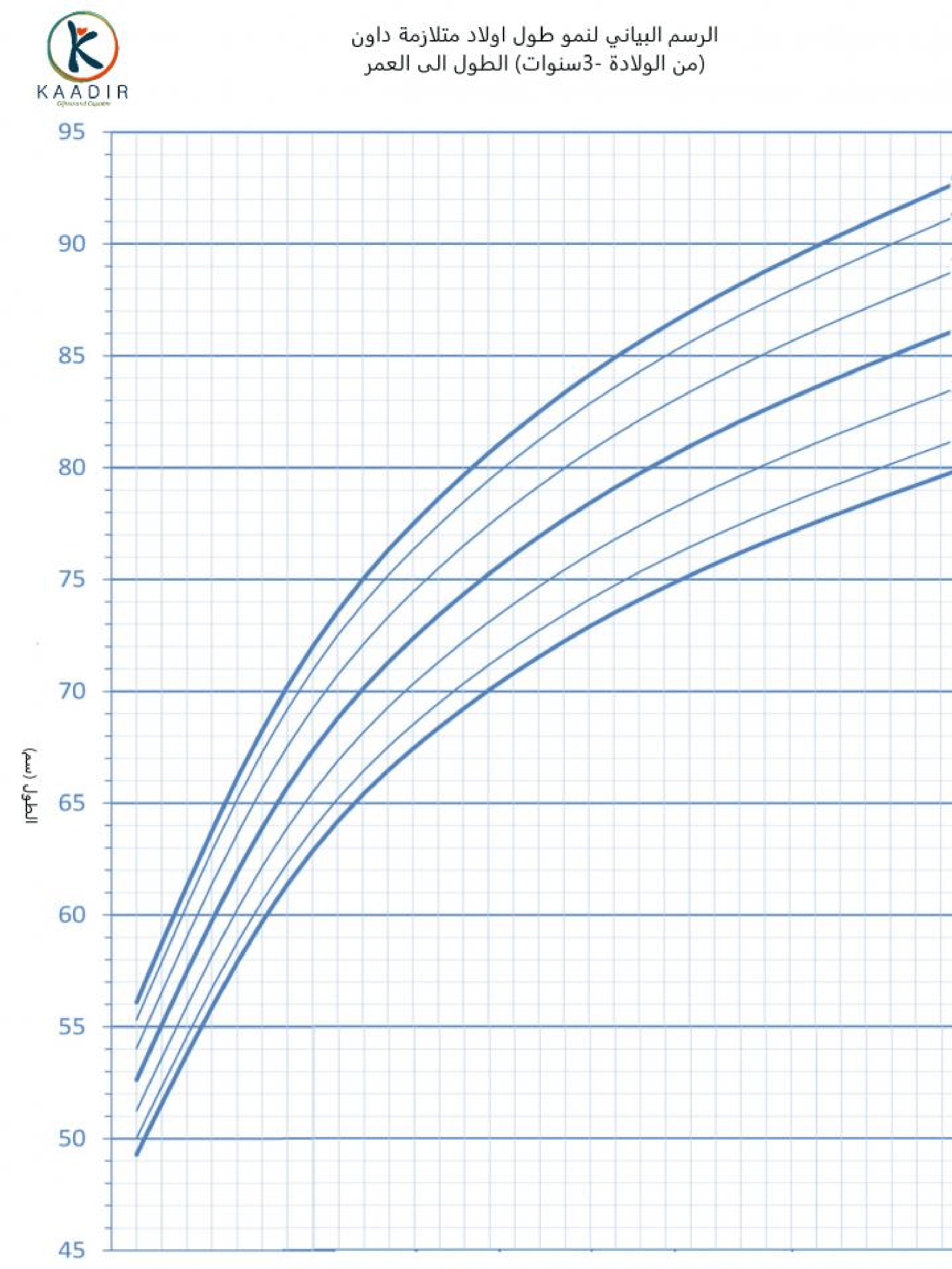
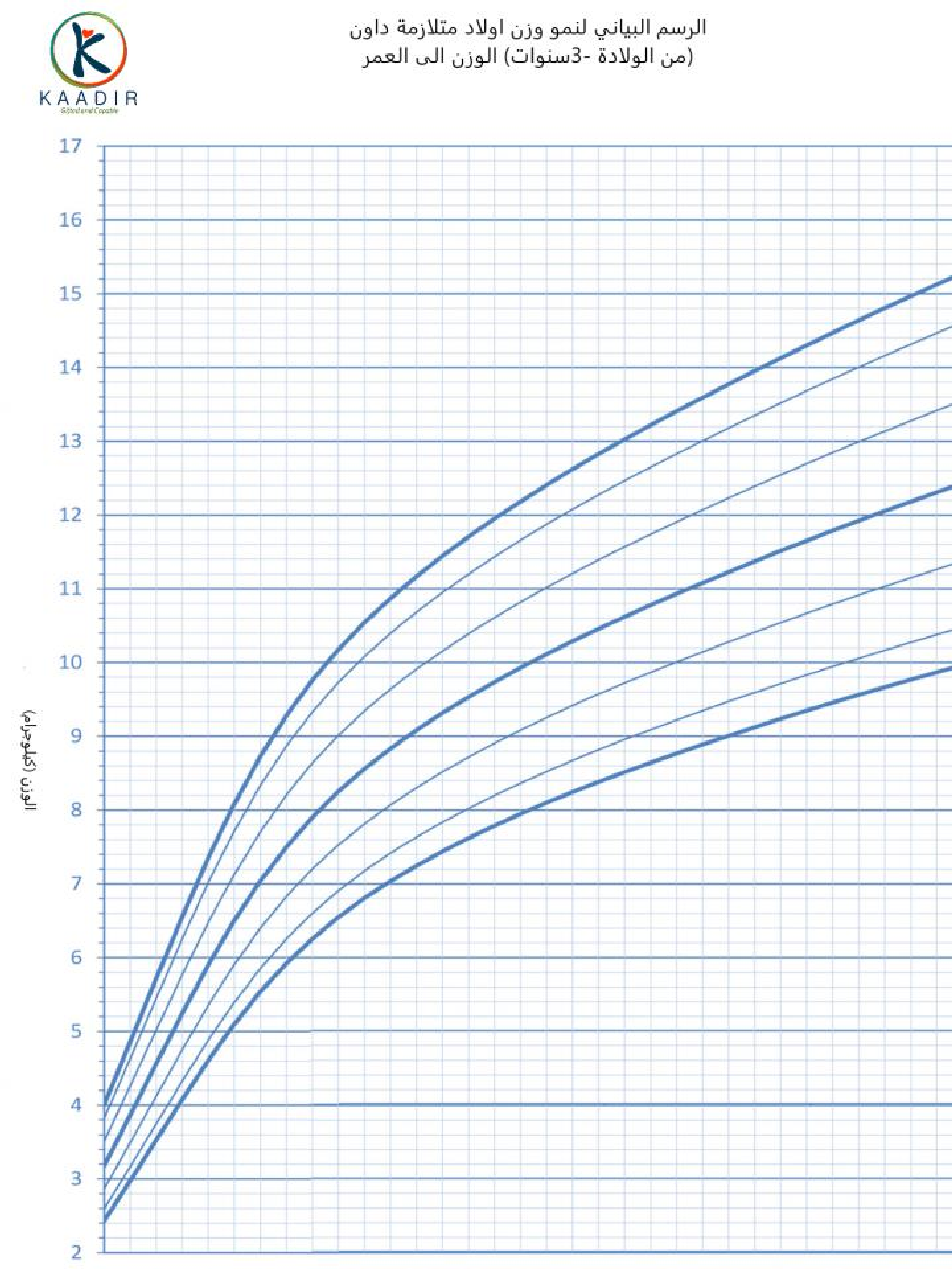
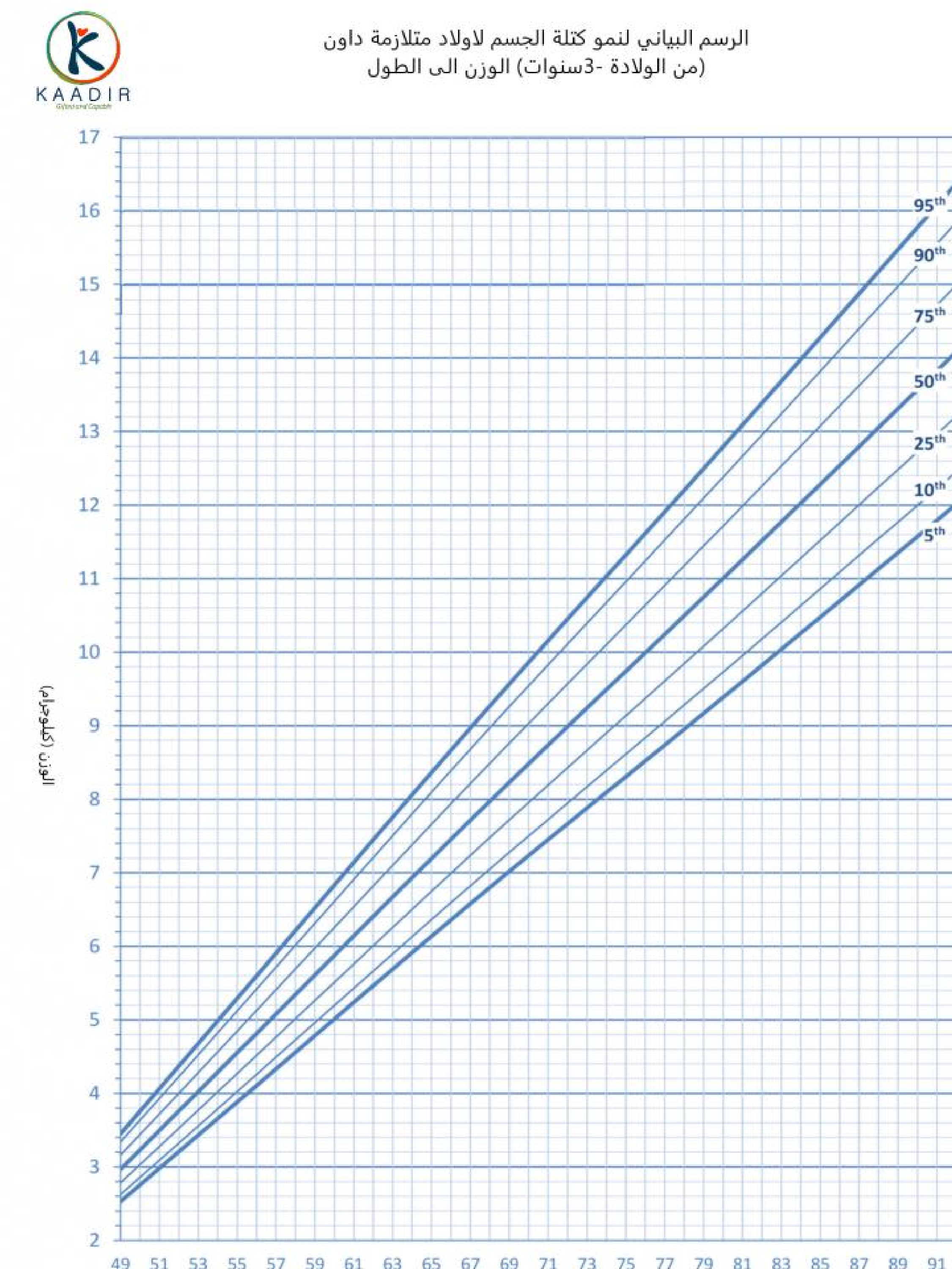
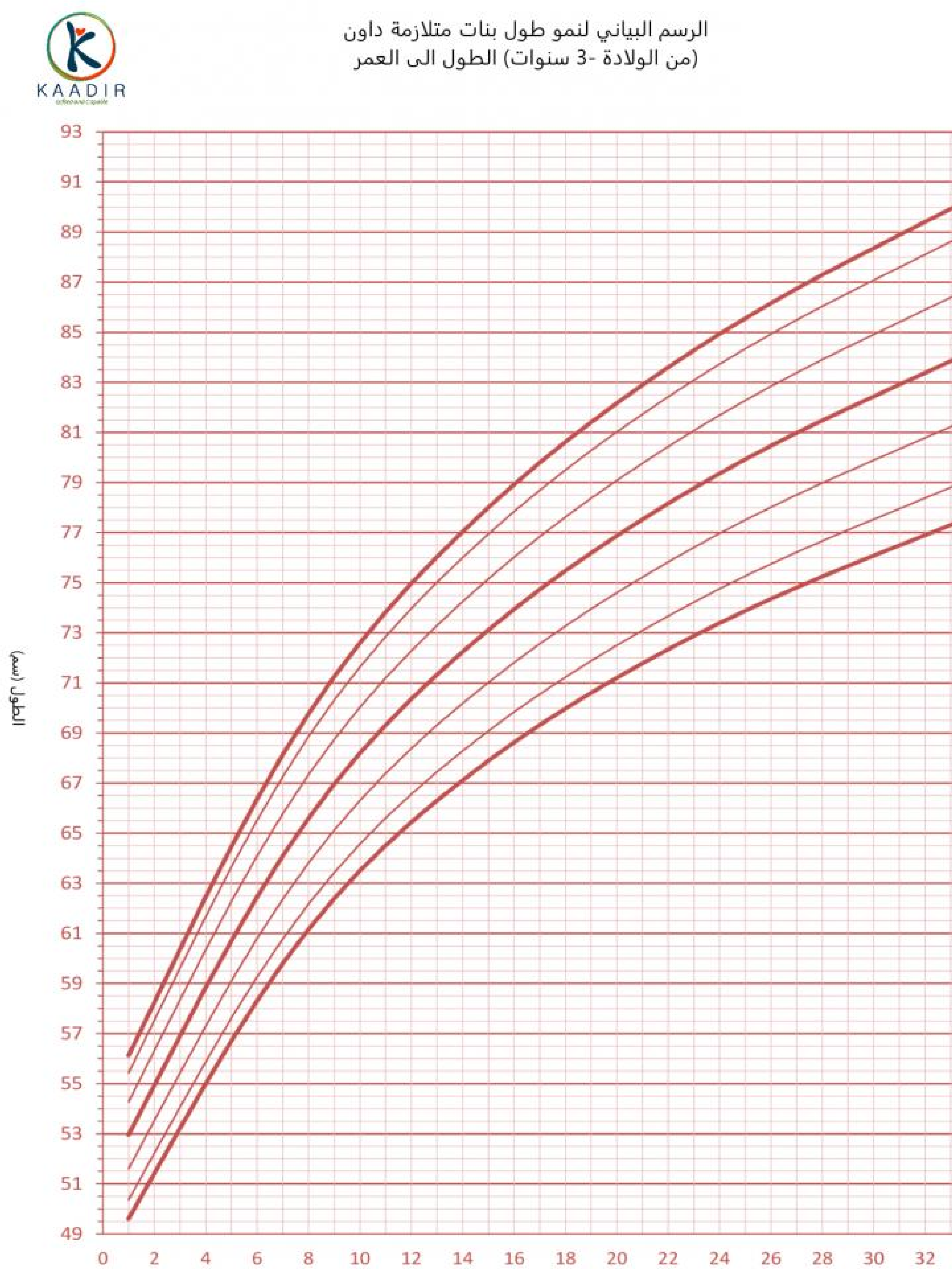
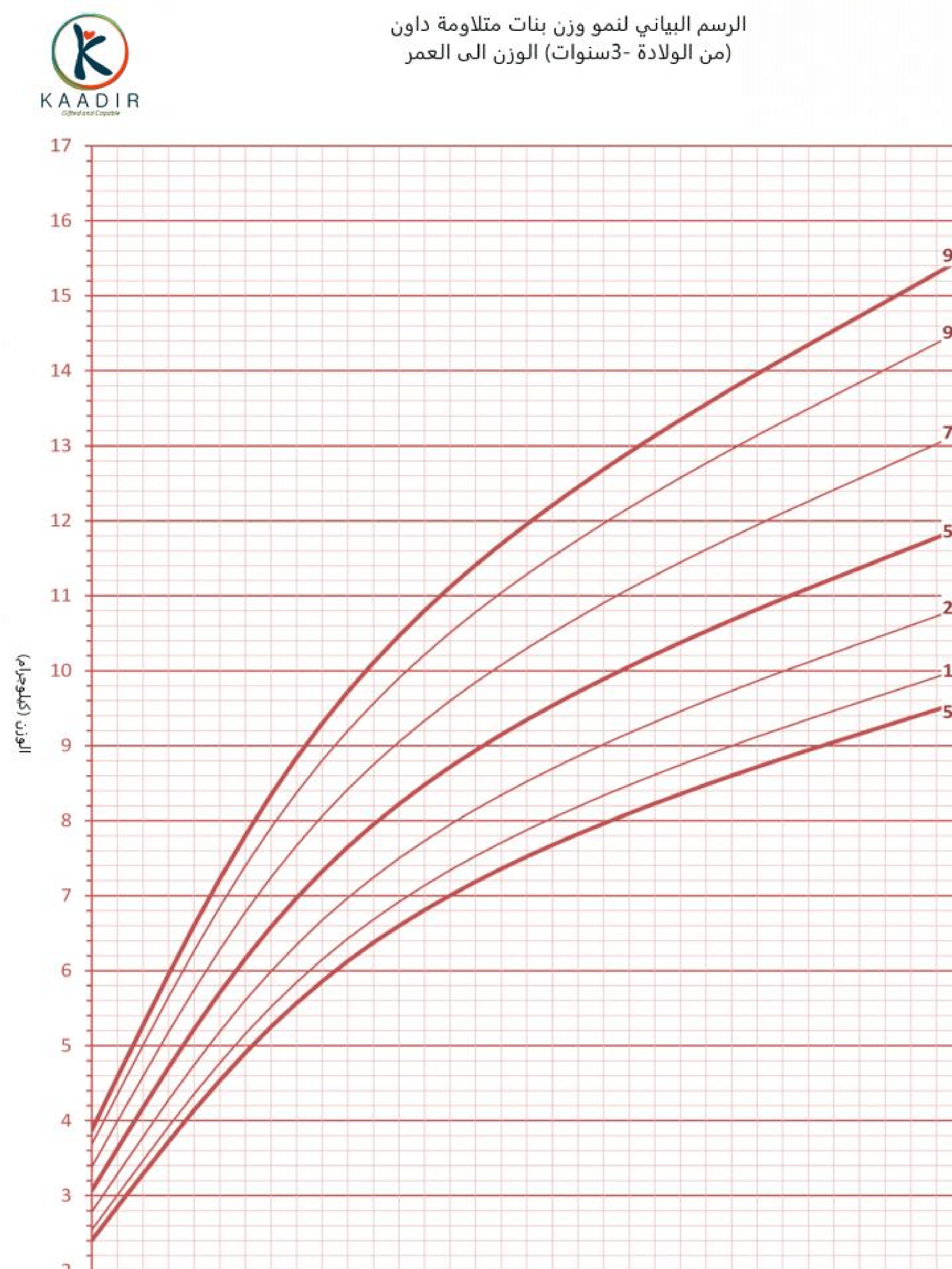
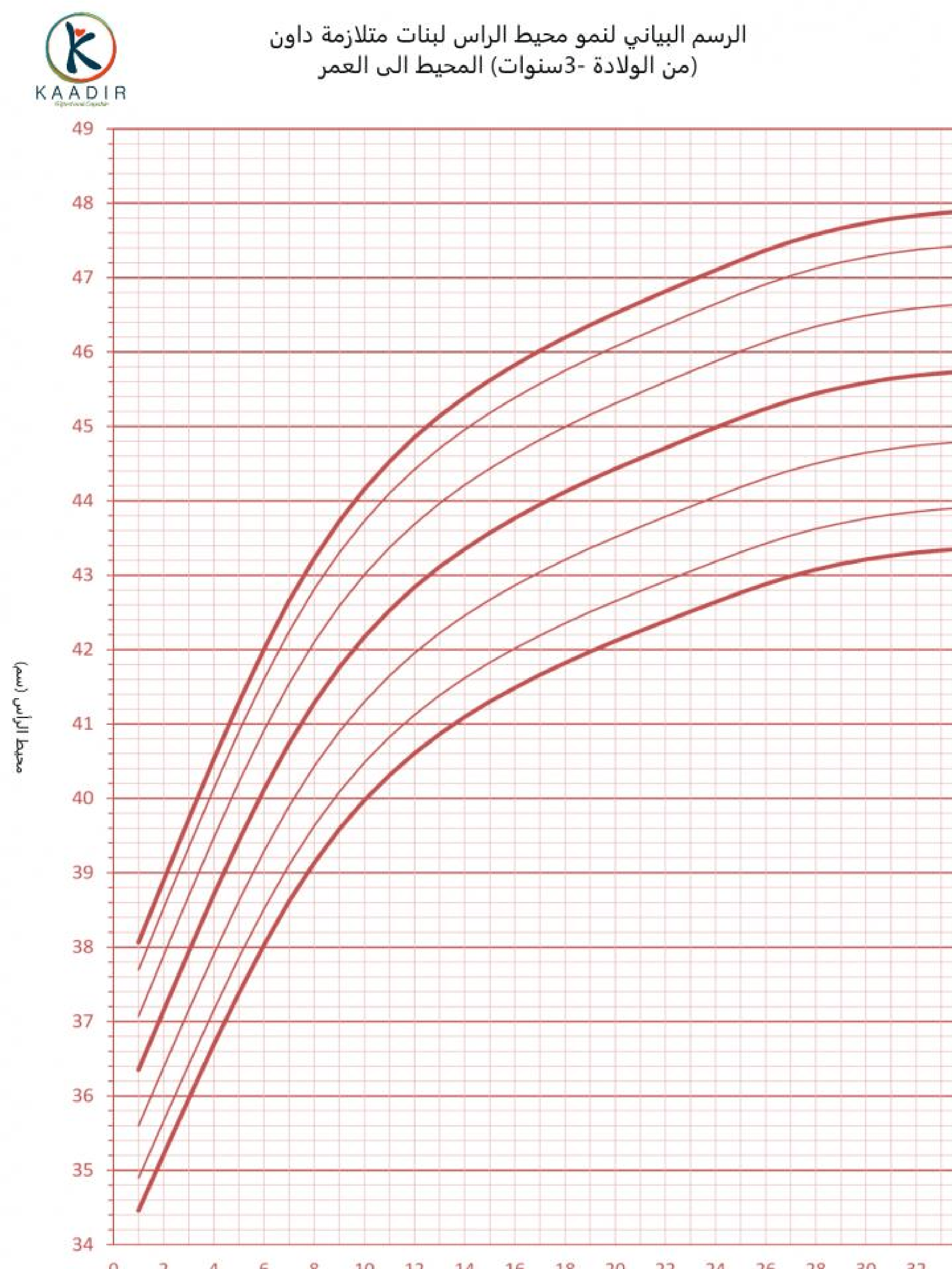
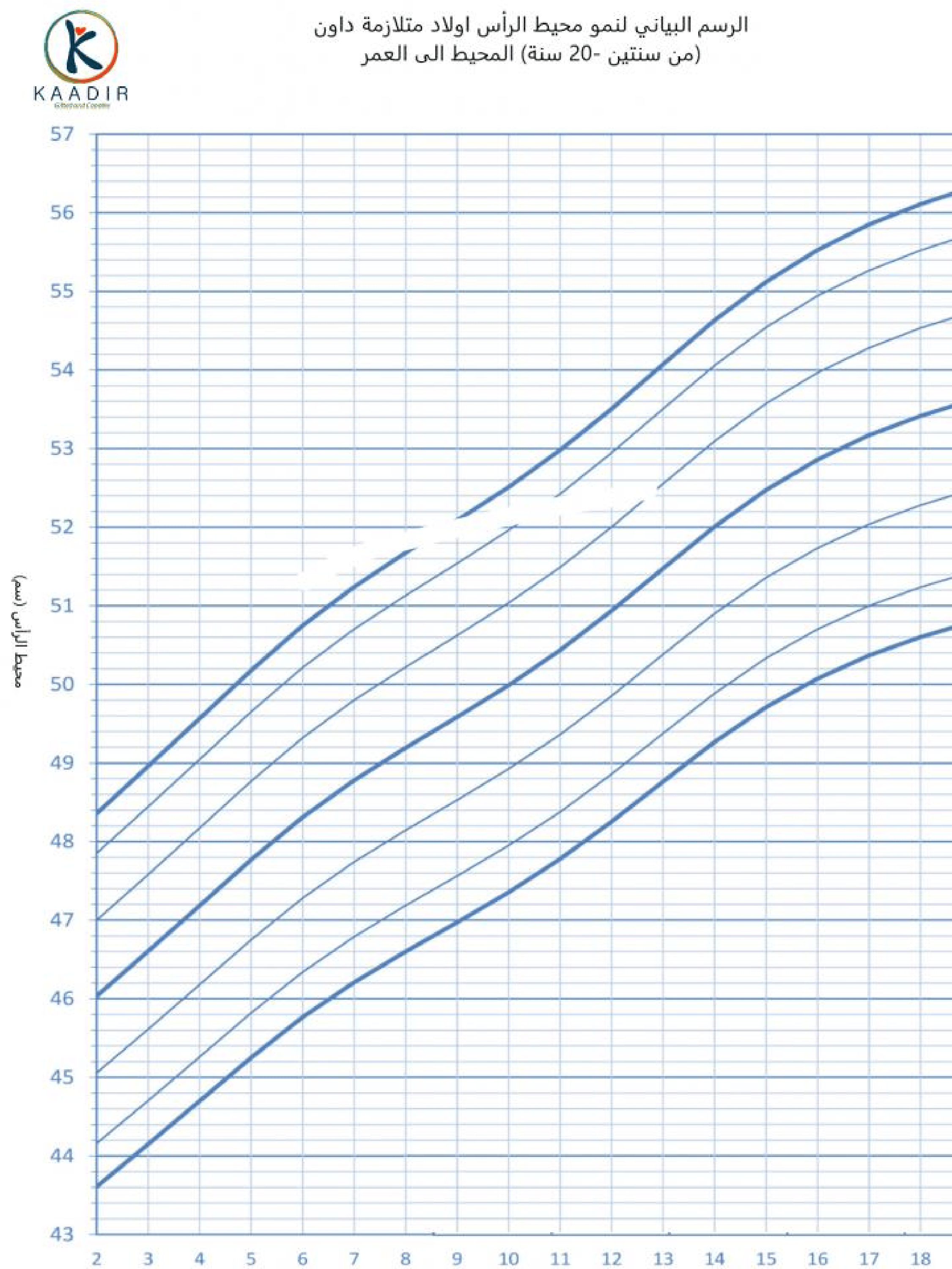
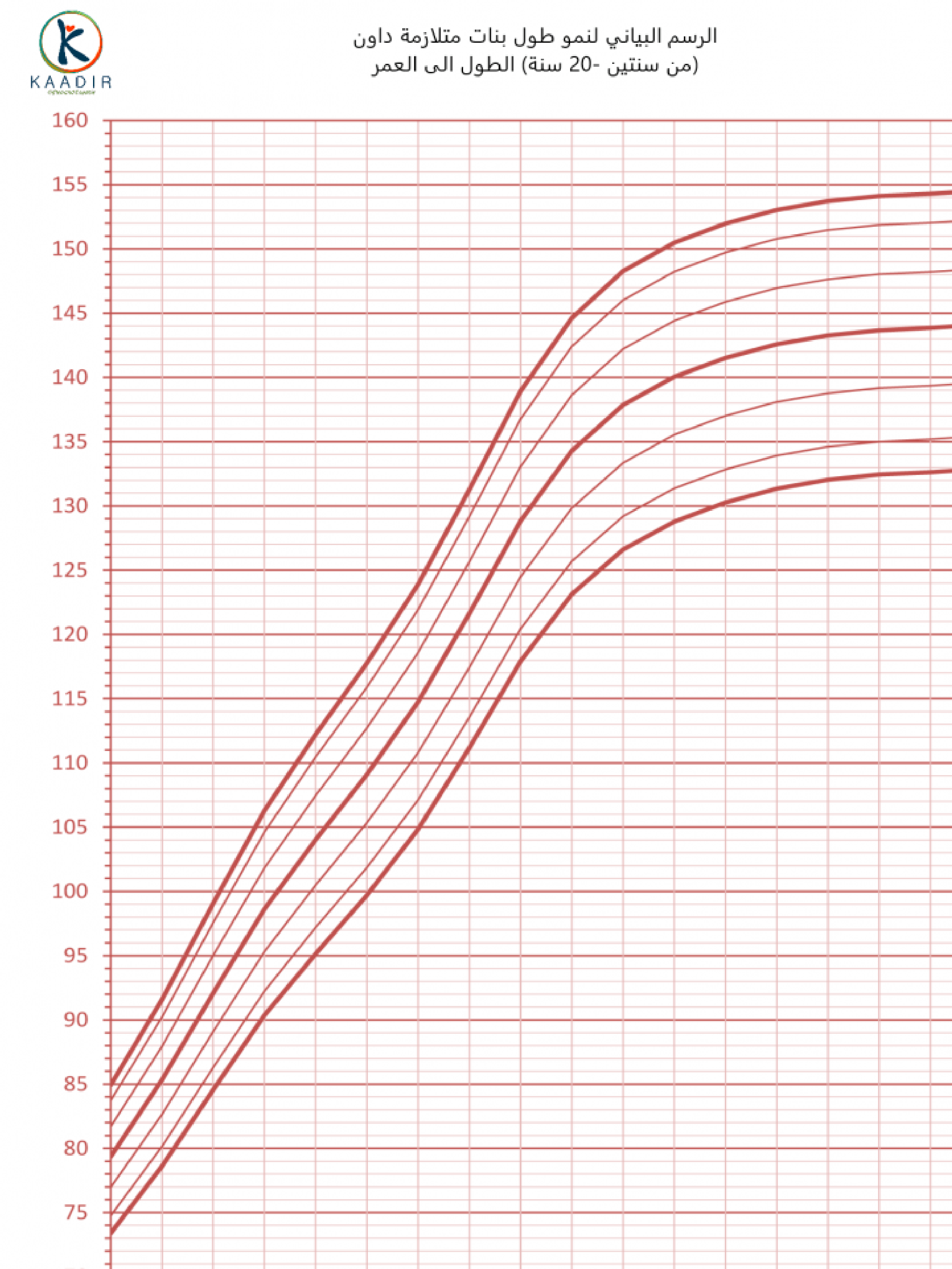
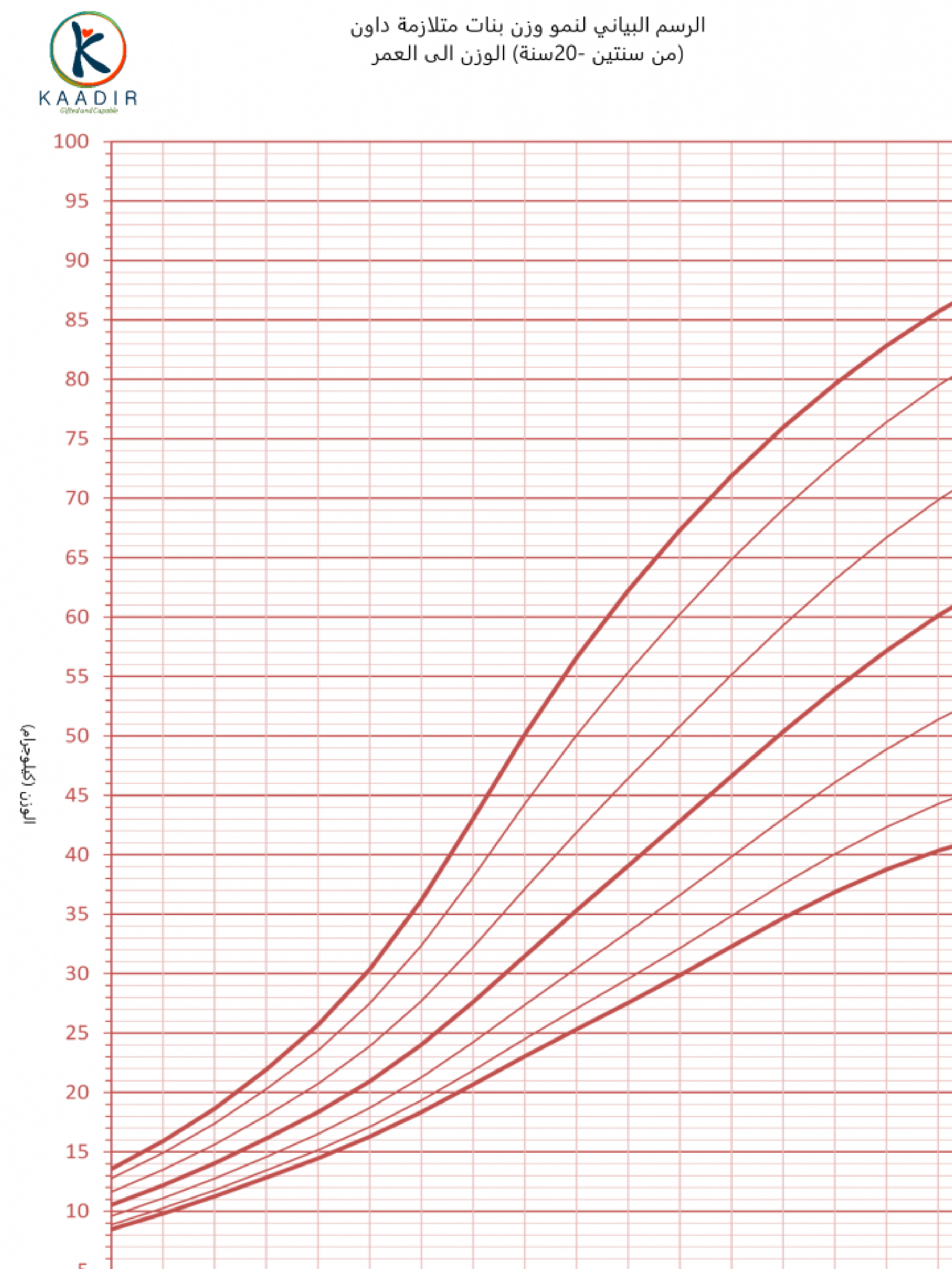
Child Growth Chart :
Parents always worry about the weight and height of their children. They compare it with other children of the same age to ensure that they are developing normally. Diagrams are a way to track a child’s physical development. Diagrams of height, weight, and head circumference (an indicator of brain development) allow doctors and parents to see if a child is growing faster or less than the typical rate.
When the doctor measures your child, he will not only tell you about the results, but also about the percentage of each measurement (the percentage number means that your child exceeds that percentage of children of his age, for example, if the percentage is 95, then this means that your child is 95 percent taller than other children of the same age) than The important thing to understand is that the best growth charts are used to track your child’s growth over time or to find his growth pattern. Determining the weight and height of your child at various ages and knowing whether he is following a steady growth curve is more important than his centenary at any time.
How to read the chart :
In the first, determine the age of the child at the bottom of the diagram and draw a vertical line (from the head to the top), then determine the weight of the child and draw a horizontal line (from the north to the right), then from the point where the two lines intersect, look for the closest curve passing from this point and continue this Conclusion oriented, find the percentage
Boys growth charts 0-3 years :

Girls growth charts 0-3 years :

Boys growth charts 2-20 years :
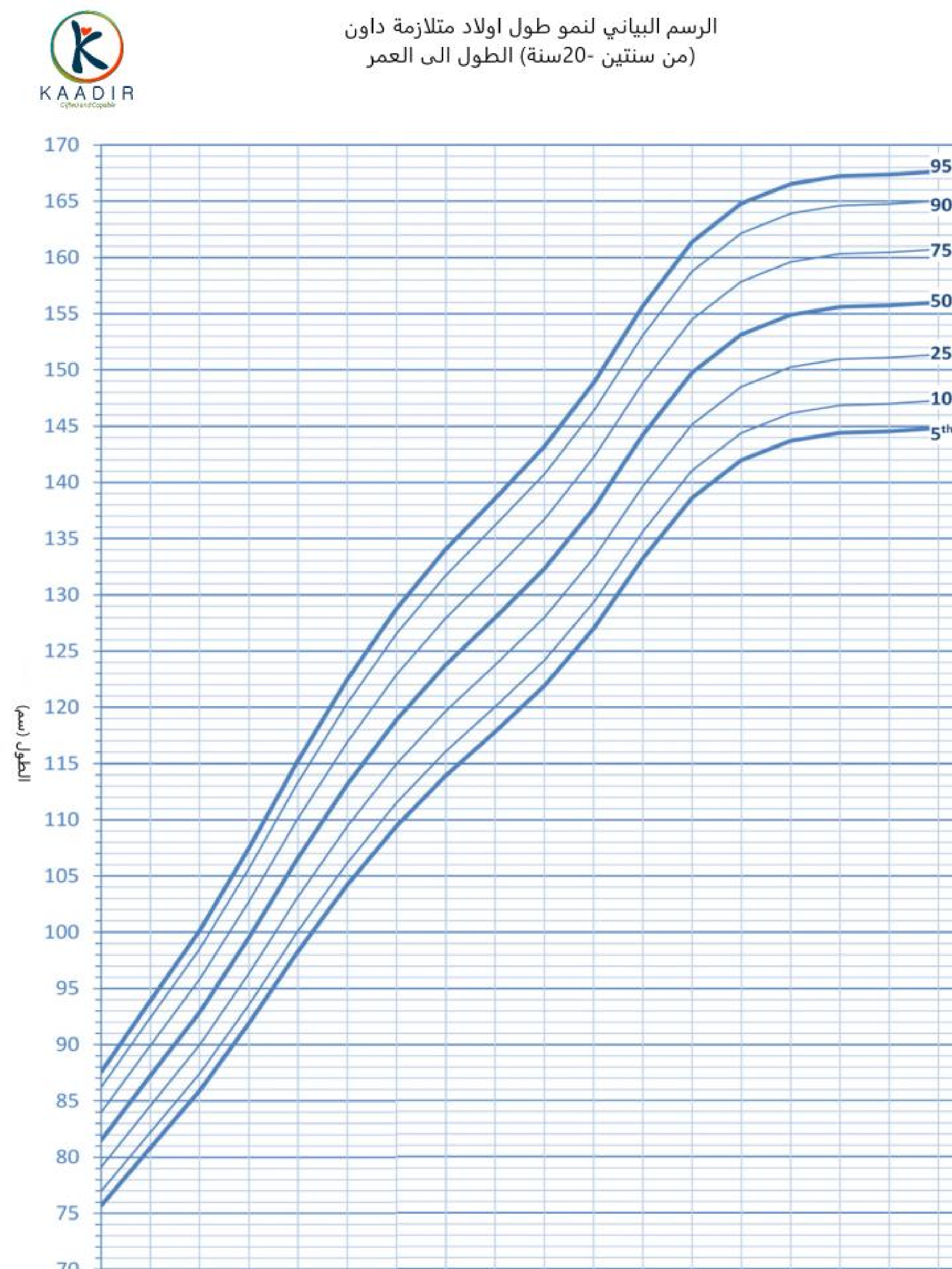
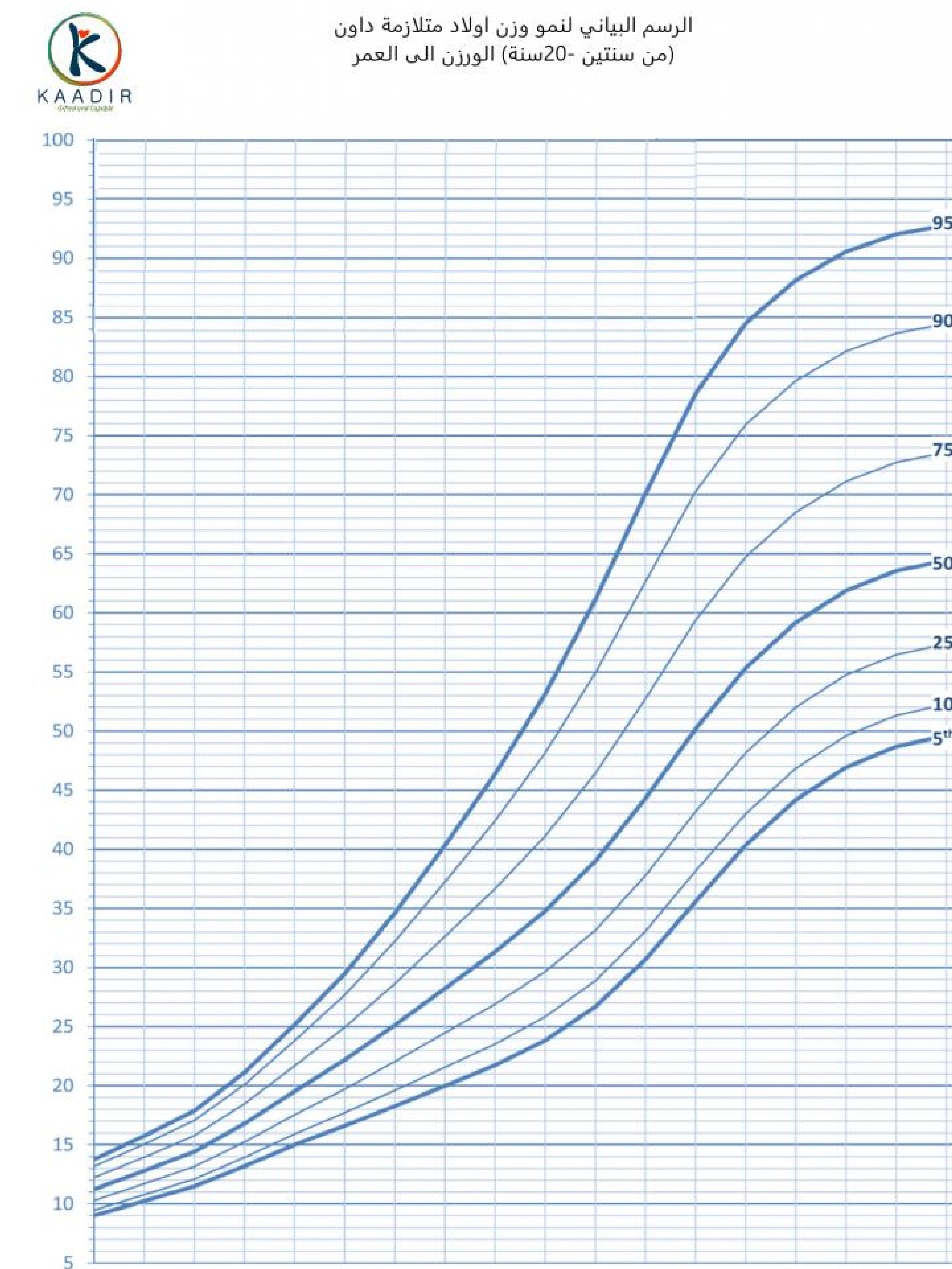
Girls growth charts 2-20 years :
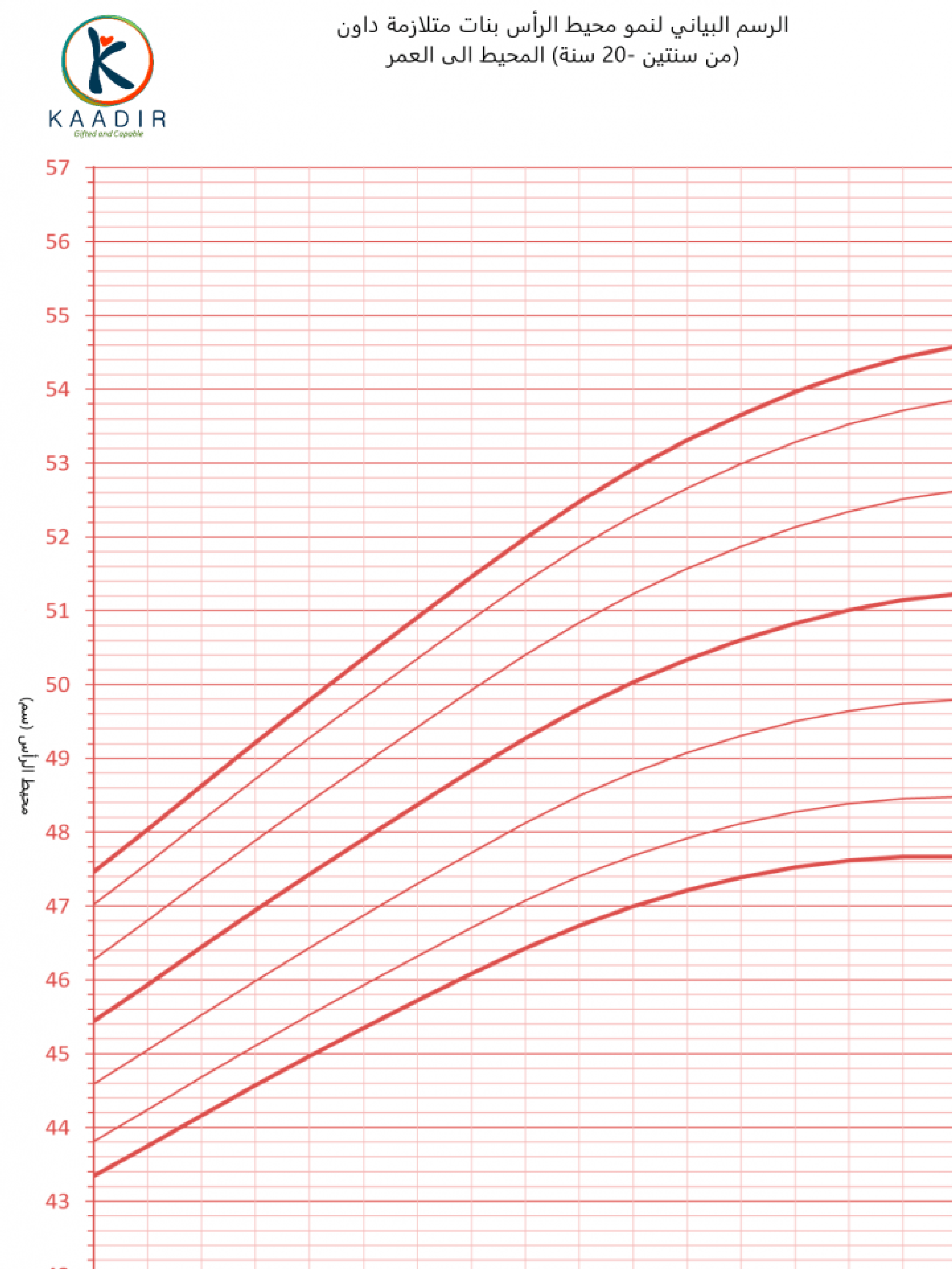
Social Development:
The social functioning of babies and children with Down syndrome is relatively less delayed than other areas of development. Babies with Down syndrome look at faces and smile only a week or two later than other children and they are usually sociable infants. Infants with Down syndrome enjoy communicating and make good use of non-verbal skills including babbling and gesture in social situations.
Most children and adults with Down syndrome continue to develop good social skills and appropriate social behavior, though a significant minority may develop difficult behaviors, particularly those with the greatest delays in speech and language development.
Learning with visual supports:
Research suggests that people with Down syndrome learn better when they can see things illustrated. This finding has been demonstrated across a number of areas of development including the acquisition of language, motor skills and literacy. This suggests that teaching will be more effective when information is presented with the support of pictures, gestures or objects.
Word reading:
Many children with Down syndrome can develop reading abilities in advance of what might be expected for their cognitive and language levels. Reading makes an important contribution to vocabulary and language development for all children and this may be a particular benefit for children with Down syndrome, given their specific language delays.
Physical growth:
Physical skills grow at a slower rate in children with Down syndrome, and these delays in physical development reduce the infants’ chances of exploring and learning about the world around them, which affects physical on their mental development. Poor movement control of the mouth may lead to an increase in language skills.
Expressive language, grammar and clarity of speech:
- Children with Down syndrome had specific delays in learning to use speech compared to nonverbal comprehension. Of course, expressive language in almost all children lags compared to language comprehension, so comprehension is what comes first. Children face two types of articulation difficulty: delays in mastering sentence structure and grammar, and certain difficulties in the development of clear speech production.
- The gap between children’s ability to understand and their inability to express themselves clearly causes frustration and may sometimes be the cause of behavioral problems. It may also lead to a misunderstanding of their mental abilities and the belief that they are worse than they really are. Linguistic delay also leads to mental retardation, as much of human learning is through language that dwells on thinking, remembering, and selfregulation.
Numerical skills:
Most children with Down syndrome struggle to acquire basic numerical skills, and their numerical skills usually delay reading skills by two years, and there is a need for research work to find out the reason for this. For the time being, the best advice is to take advantage of what is known about the strengths of children’s learning and to use mathematics learning systems that use visual aids to teach number concepts.
Short-term verbal memory:
- Short-term memory is a system of direct memory that keeps information “in the mind” for short periods of time and is a pillar of all learning and mental activity processes. And this memory has different components, each one of which is concerned with processing visual or verbal information.
- Children with Down syndrome are less able to retain and process verbal information than they are to retain and process visual information. These short-term verbal memory problems make learning new words and phrases more difficult, and spoken language difficult to understand, which may negatively affect learning in the classroom.
- Studies indicate that understanding and remembering spoken information improves when using images related to the information to be communicated. This research result has prompted those in charge of education to emphasize the importance of using visual aids, including pictures, signs and prints, when teaching children with Down syndrome, because this approach makes full use of their stronger skills in visual memory. People with Down’s syndrome learn visually, meaning they learn more easily from visual information rather than verbal information, and the use of sign language and reading actually proves to improve the speech and language development of children and adults with Down syndrome. Sign language from childhood and reading singing may use an actual method for learning the language from the second year. Because learning to speak supports other mental abilities such as perception, education and thought. If children with
Down’s syndrome accelerate the development of speech and language, then their mental abilities will improve and the speed of education will be improved.
Playing games :
The other important way in which they learn is play. From what we see during childhood and afterward, children with Down’s syndrome learn by playing like any other child, but they benefit from more help. It is important that you interact with them and participate in the games for the sake of encouragement. You must remember that they may not understand everything you say to them, but they strive to observe and learn by imitation.
Social education and behavior:
Children whose development is delayed, especially if they lag in their linguistic abilities, are at risk of adopting unacceptable behaviors. However, most boys with Down’s syndrome are not difficult to deal with them further than others and behave in ways that are acceptable and socially acceptable. However, some behave in less appropriate ways that may cause stress because they interfere with a happy family life.
Health care during childhood :
It is important to have regular medical examinations during childhood for those who have children:
- Conducting medical examinations of the heart
- Regular check-ups and regular audiovisual care
- Periodic examinations of the thyroid gland
References :
Mayo Clinic https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/downsyndrome/growth–charts.html https://www.dsastx.org/wp–content/uploads/2018/09/DS–Developmental–Milestones.pdf
https://www.clinicalguidelines.scot.nhs.uk/media/2618/health–assessment–of–children–and–youngpeople–with–downs–syndrome–paediatrics.pdf
كتاب متلازمة داون حقائق وارشادات وحروف من القلب
Adolescence And Young Adulthood
Unlike the rumors about Down syndrome, adolescents and young adults enjoy an integrated life, so they can be influential people in society and enjoy complete independence. Like any person, people with Down syndrome need support, encouragement, and help to achieve their dreams. With the right support, they can enjoy a rich and fulfilling life and feel a part of their communities. There are now more options than ever before for jobs and living arrangements. The challenges they face may increase in proportion to health problems caused by the extra chromosome. These challenges differ from one person to another and vary in their degrees and the extent of response to treatment in each case.
Most adults with Down syndrome can lead healthy lives. To achieve this goal, this requires an integrated system that includes living a healthy lifestyle, following certain preventive measures, participating in a health examination, and treating health problems early in their discovery. While there are some disorders that occur more commonly in people with Down syndrome (and some occur less frequently), following this regimen is a way to enable them to lead a healthy life.
Modern science has developed in its study of Down syndrome, and all studies have concluded the importance of early intervention from an early age to develop cognitive and speech skills and focus on physical therapy to develop their abilities and enhance their ability to work and socialize.
On this page, we review some of the common challenges facing adolescents and adults with Down syndrome, and we will in Kaadir search and explore solutions that can be adopted to move forward in life, and specialists are available to answer all questions and inquiries.
Alzheimer’s:
People with Down syndrome are three to five times more likely than other people to develop Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s disease may begin at an early age of 30 years for people with Down syndrome compared to the age of 50 for the rest of the population. There are various symptoms of other diseases and conditions that mimic the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, such as a change in personality, a decline in daily living skills, memory loss, changes in coordination and walking, and other changes. Diseases and conditions such as depression, thyroid disorders, brain tumors, recurrent strokes, and various metabolic imbalances. Therefore, neurological conditions must be excluded before the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease.
It is recommended that people with Down syndrome undergo a basic cognition test at age 30, and that this test be repeated annually to identify any deterioration in this function. Some symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease can be treated, although not present
Sensitive Degenerations :
People with Down syndrome are exposed to a lack of sensory skill that may affect development as it reduces the ability of children and adults to understand their surroundings and learn, and if untreated, it may cause a delay in the individual’s development.
Hearing loss:
The occurrence of a slight or moderate loss of hearing ability among children with Down syndrome is not negligible, as between 70 and 80 percent of children suffer from conductive dysfunction to various degrees.
The loss of between 25 and 40 decibels or more of the hearing ability in children with Down syndrome due to a defect in the middle ear is normal, which leads to difficulties in learning the language during childhood and the early years. A loss of 25-30 decibels affects hearing ability in a classroom or noisy environment.
Hearing loss affects people with Down syndrome negatively, as adolescents become moody, and it may affect their academic achievement as well. Therefore, they must be monitored continuously and focus on periodic examination in order to be able to quickly intervene and adopt the necessary treatment to avoid all problems.
Vision :
Visual impairment (vision) is a common problem as it is in the general population. However, an adult with Down syndrome may have difficulty recognizing the problem or communicating it to someone who can help. If work skills or other daily skills deteriorate, the cause could be as simple as decreased eyesight.
Adults with Down syndrome are at risk of developing premature cataracts and keratoconus. Cataracts cause clouding of the eye’s lens, resulting in blurry and poor vision. Keratoconus causes the round cornea to become conical in shape, which can distort vision. Both conditions can be examined by an ophthalmologist and should be evaluated regularly.
Undiagnosed sensory impairments (vision or hearing) are often considered stubborn, and this condition is very common. And when properly diagnosed, it can be greatly improved with eyeglasses, hearing aids, and ear cleaning
Thyroid :
The thyroid gland contributes to controlling various metabolic processes, the speed with which the body uses energy, synthesizes proteins, and regulates hormones. Hypothyroidism is common in adults with Down syndrome and can lead to symptoms of fatigue, mental lethargy, weight fluctuations and irritability.
Being overweight:
Obesity is more common in people with Down syndrome. A recent study found that children with
Down syndrome have a basal metabolism rate lower than the general average, and people with Down syndrome burn 200-300 calories less than average. So it is essential to burn these calories daily through increased activity to prevent weight gain. In addition, it is better to offer options such as fresh fruit or vegetables, and low-fat foods such as popcorn or pretzels, rather than serving candy or snacks.
In order to achieve better long-term success, the principles of good general nutrition and regular exercise must be followed. It is recommended to do aerobic exercises for at least twenty to thirty minutes three days a week. Aerobic exercises include activities such as walking, running, swimming and cycling.
Spine problems :
People with Down syndrome are usually very flexible. Over the years, this can increase the wear of large joints (hips, knees, etc.). This increases the risk of developing osteoporosis, especially for adults who are overweight or previously overweight. They are also at risk of developing painful arthritis, which in turn can lead to decreased mobility and decreased desire to participate in activities. For some, pain can manifest itself through negativity or behavioral changes. Untreated pain increases the risk of increased immobility
Osteoporosis causes the bone mass to thin, which increases the risk of the fracture. People with Down syndrome are more likely to have this, especially if there is a lack of movement or a family history of osteoporosis, early menopause, or prolonged exposure to some anti-seizure drugs. Osteoporosis is screened for by bone density test and can be treated with medication as well as other exercise and lifestyle adjustments.
Celiac disease :
Celiac disease (wheat allergy) is a condition in which the body cannot digest wheat gluten and wheat products cause damage to the intestinal lining, and when this disease is present, it can cause severe intestinal pain. People with Down syndrome are more likely to have this disease. Celiac disease can be examined with a blood test but requires a bowel biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. Therefore, a visit to a gastroenterologist is essential in order to make the diagnosis. Celiac disease is usually treated primarily with a wheat-free diet.
Other health issues adults with Down syndrome tend to face include:
- Diabetes
- Early menopause
- High cholesterol
- Increased risk of leukemia
Adulthood:
The transition from childhood to adulthood is a difficult period in children’s lives, especially for people with Down syndrome. People with Down syndrome have a range of sexual feelings just like any teenager. These physical and emotional changes can be difficult to understand. Teens may struggle to understand when it is appropriate to talk about these changes and who is the right person to talk to about them. Teens with Down syndrome undergo the same changes in adulthood as all teens do. All teens, it is important to teach children with Down syndrome what to expect during these years, especially as their bodies change, and these teens begin to explore their sexuality.
Taking care of personal hygiene becomes a priority for both boys and girls, and helping them become as independent as possible in this area is a must, it may take a little longer, although these changes may be delayed a little for boys with Down syndrome. While the overall fertility of men with Down syndrome may decline dramatically, there is still a possibility of marriage and childbearing as well
For girls, this is when their period starts and they have to learn to manage it. It is important for them to know in advance what to expect, why this is happening, and what they should do when their period starts. At least 50% of women with Down syndrome enjoy childbearing. Education is an appropriate and highly desirable component of positive gender development and awarenessraising
Sleep :
As everyone ages, there are expected changes in sleep habits. Staying asleep is more difficult, especially for older people who wake up frequently during the night and early in the morning. The amount of deep sleep is less than that of young adults. With these changes comes an increase in daytime sleepiness and naps. Other medical problems such as disrupted sleep and irregularity in the body’s natural sleep cycles can start.
The Routine :
One of the most interesting observations noted is that people with Down syndrome with Down syndrome need symmetry, repetition, and order in their lives. This repetition is the “routine” that people’s thoughts and actions tend to follow the routine fairly well.
Types Of Routine :
One of the most common routines is the specific pattern or daily routine of activities. Many of them often have systematic and meticulous morning habits of dressing and grooming in addition to their daily work routine. So is the evening routine to relax and prepare for sleep. Many people with the syndrome have also been found to be keen on taking care of their rooms. There is also a wide range of other routines, the most common of which are personal preferences for things like music, sports teams or celebrities.
Advantages Of Routine :
There are many advantages to routine, one of which is that they give an important sense of order. It also helps them take control of their lives. In addition to that, routine helps to organize and manage daily living tasks, and this increases their independence. Once an activity is learned and it becomes part of the daily routine, supervision from others is rarely needed. The routine also provides a haven from the stresses and strains of everyday life.
Disadvantages Of Routine :
Although there are many benefits and advantages, there are also some drawbacks to the routine .That causes minor problems sometimes. For example, a person may be interested in a specific issue such as as a favorite sports team they bring up again and again with family and friends. While this may be a slight inconvenience to some. In addition, there are routines that may be adaptable if done in the right place and time. For example, a bathroom cleaning routine may be greatly appreciated by family members unless it is done in the morning when everyone in the family needs to be ready for work.
Ironically, the resemblance may conflict with their need for accuracy and cleanliness. For example, some people prefer to wear the same comfortable shirt or jeans over and over again rather than a new one. Some people may fold dirty clothes and put them in wardrobes instead of in the laundry basket.
For more information, you can talk to the specialists on the Speak with Specialists page
The first years of a child’s life are among the most difficult years in terms of growth and acquisition of skills, or what is known as child growth in scientific terms. Most children go through rapid development during this period. It is in it that the physical, mental, linguistic, and social development and daily life skills that every person depends on in the future takes place. Children acquire these skills almost automatically at a certain age, which can be expected by looking at schedules prepared for this matter.
Children with Down syndrome usually face delays in some of these developmental skills, so it is advisable to include these children in early intervention programs to enhance, stimulate and help these children to acquire these skills. It is possible to join intervention programs at any time after birth, so the earlier the time, the greater the benefit. Larger
What is early intervention
It is a structured rehabilitation program of treatment, exercises and activities that focuses on the stages of growth and the acquisition of skills and contains several services, including the mobility, social, educational and psychological aspects, which are provided to children who have delays or susceptibility to developmental delay and the acquisition of developmental skills. The main ones for growth are movement, language, social interaction and daily needs skills. The services provided to children also include physical therapy, speech and speech therapy, and occupational or behavioral therapy.
Studies and research have confirmed that children with Down syndrome benefit from early intervention programs that provide training and rehabilitation services for pre-school children, since this stage is a stage of rapid development and the acquisition of basic skills and knowledge, so we were keen to be able to provide these services to the family by specialists.
What are the types of early intervention treatments?
A variety of therapies can be used in early intervention programs and throughout a person’s life to promote the greatest possible development, independence, and productivity. Some of these therapies are listed below
Physiotherapy :
Physical therapy focuses on motor development. During the first three or four months of life, the infant is expected to gain control of the head and the ability to take a sitting position (with assistance) with no head lag and sufficient upper body strength to maintain an erect position. Appropriate physical therapy can help a child with Down syndrome, who may have low muscle tone, achieve this stage.
The child’s ability to explore his surroundings, reach and hold toys, turn his head while watching a moving object, turn and crawl all depend on motor development. These physical and interactive activities enhance understanding of the environment and stimulate cognitive, linguistic and social development
Speech therapy:
Speech and language therapy is an important component of early intervention. Although children with Down syndrome may not pronounce their first words until the age of two or three years, there are many pre-pronunciation and pre-language skills that they must acquire before they can learn how to form words. These skills include the ability to imitate and repeat sounds, role-taking skills
(learned through games such as “hide and seek”), visual skills (looking at the speaker and objects), auditory skills (listening to music or speaking), touch and oral motor skills). Using tongue and moving lips), and cognitive skills (understanding the sustainability of things and cause-andeffect relationships).
A speech and language specialist can help with these skills. Breastfeeding helps in strengthening the jaw and face bites of the child and lays the foundation for future communication skills.
Occupational Therapy :
Occupational therapy helps children develop their skills and mastery to reach independence. Occupational therapy can assist with abilities such as opening and closing objects, picking up toys of different sizes and shapes, construction, and experimenting with colored numbers. Therapists also help children learn to feed and dress themselves, and teach them skills to play and interact with other children.
Behavioral therapy :
Emotional and behavioral therapies work to find useful responses to both desirable and undesirable behaviors. Children with Down syndrome may become frustrated because of difficulty communicating, may develop compulsive behaviors, and may have Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and other mental health issues. These types of therapists try to understand why a child is acting out, create ways and strategies for avoiding or preventing these situations from occurring, and teach better or more positive ways to respond to situations
Educational therapy :
Most of the educational therapies used to address the core symptoms of Down syndrome are provided through programs run by states and local school systems. It’s important for parents and teachers to understand that no single educational approach is right for every child. Most children with Down syndrome can spend at least some of their time in a general education classroom with typically developing peers but some children can benefit from a smaller setting with more individual support.
Assistive Devices:
More and more often, interventions for children with Down syndrome involve assistive devices— any type of material, equipment, tool, or technology that enhances learning or makes tasks easier to complete. Examples include amplification devices for hearing problems, bands that help with movement, special pencils to make writing easier, touchscreen computers, and computers with large-letter keyboards.
Assistive Technology is playing an enabler role in the life of Dawn Syndrome. Assistive Technology can allow Down syndrome to engage in the normal life activities and be more social and independent. For example, it helps them remember the important stuff, it help them read and write, it can help them take notes or edit documents and much more.
Early Intervention Video Series
Speech Therapy Videos by Basent Hussam Eldin
Abstract
Inside the cells of our bodies there are small structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes carry The genes that determine how we grow. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in every cell and the normal human body consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes; So that each pair of these chromosomes consists of a chromosome that comes from the mother, while the other chromosome comes from the father.
What is Down syndrome?
Down syndrome, a congenital condition, defined as a genetic disorder that occurs as a result of a defect in the abnormal division of chromosome 21, which leads to a person with this syndrome having a complete or partial extra copy of the 21st chromosome
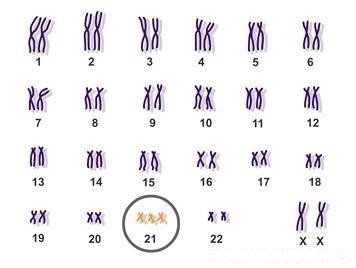
Types of the syndrome:
Trisomy 21 (trisomy, triple syndrome):
accounts for about 90% of cases. Where a person has an extra chromosome (chromosome 21), they have three 21 chromosomes, instead of two copies.
Mosaic Down syndrome:
It is considered one of the rarest types, in which a person has an extra copy of chromosome 21, in some of the individual’s cells, but not all As a result of abnormal cell division after fertilization.
Transition, or Down Syndrome:
This type occurs when part of chromosome 21 becomes attached to, or attached to, another chromosome
The psychological effects of the mother
Motherhood is a beautiful feeling that exists within every mother from the moment of knowing her pregnancy and then following its development moment by moment and waiting for it to come anxiously. The mother usually begins to build perceptions about this child who has not yet seen the light of our fetus. And you feel a lot of longing to see him, imagine his looks, and dream about his future .Most mothers are traumatized by the birth of a child with Duane syndrome, as suddenly this challenging child does not fit the imaginative child without challenges that they imagined before birth. Which affects the psyche of the mother, who is disturbed and her feelings diverging .As soon as the mother knows about her child’s condition, a series of psychological and social pressures begin, and the accompanying depression, anxiety, remorse and fear of the future, which represents the biggest unknown concerns of the mother. We at Kaadir will provide you with all the support you want and everything related to Down syndrome so that you can help yourself and your child. It is very important for the family to have a high spirits so that this spirit transmits to the child and helps him to move forward.
Health complications for people with Down syndrome
There are several medical problems that are commonly found in people with Down syndrome. Usually these are not major problems in and of themselves, but they can affect health and growth and must be examined so that early diagnosis and treatment can be made. It is important for every person with Down syndrome that these medical problems are recognized and treated even though your child may not suffer from it. Any of these potential complications it is important to be aware of them so that you can understand them early in the event they occur, especially for those who suffer from heart problems as the delay in growth may be attributed to poor health and hospitalization due to the heart and thus may be overlooked About other problems. People with Down syndrome may have a range of complications, some of which become more prominent as they get older
Although the list of potential health problems can be frightening, you must bear in mind that your child will not necessarily suffer from all of them or perhaps any of them. Health care, routine checkups and treatment when needed help maintain a healthy lifestyle for people with Down syndrome. Attention must also be paid to healthy nutrition for people with Down syndrome, including breastfeeding
Recommended Medical Test
Regular check-ups and tests will help to know if your child is suffering from any health problems or needs treatment, in many cases your child’s health is better when his health problems are discovered and addressed early


